24-Mar-2025
Single Girder Overhead Crane and Electric Hoist Installation Construction Plan
Introduction
Single girder overhead cranes and electric hoists are indispensable lifting equipment in modern industry. The rationality and precision of their installation and construction plans directly affect the operational efficiency and safety of the equipment. In a highly industrialized country like Singapore, the installation and maintenance of lifting equipment are particularly important. This article will detail the entire process from equipment and material preparation to on-site installation layout, specific installation steps, commissioning, and final safety inspections and acceptance. Through meticulous planning and strict operations, the stability and efficiency of single girder overhead cranes and electric hoists in various industrial production scenarios are ensured.
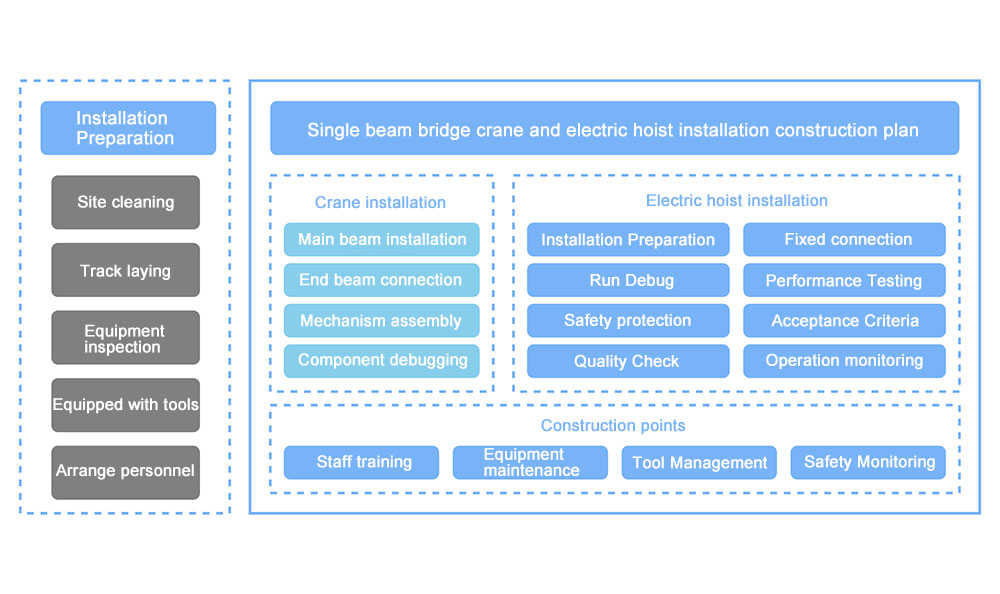
Overview of the Installation Construction Plan
Single girder overhead cranes and electric hoists are critical lifting equipment in modern industrial plants. The formulation and execution of their installation and construction plans directly impact the stable operation and safety of the equipment. This plan aims to elaborate on the installation process, technical requirements, and safety measures for single girder overhead cranes and electric hoists, ensuring a standardized, efficient, and safe installation process. Through systematic planning of pre-installation preparations, on-site layout, installation steps, commissioning, and acceptance, high-quality installation of the equipment is achieved. Additionally, this plan emphasizes quality control and safety protection measures during installation to ensure the safety and smooth progress of the entire process.
Equipment and Material Preparation
Inspection of Single Girder Overhead Crane Components
Before formal installation, a thorough and comprehensive inspection of all components of the single girder overhead crane is required. This includes, but is not limited to, the main girder, end girders, hoisting mechanism, traveling mechanism, electrical system, and other key components. For the main girder and end girders, the inspection mainly covers the integrity of the components, such as cracks, deformations, and other surface damages, as well as dimensional accuracy and fit clearance. For the hoisting and traveling mechanisms, the tightness of various components, such as bolts and nuts, must be checked to ensure they are not loose or missing. The wear condition of components like gears and bearings should also be inspected, along with the lubrication status, ensuring sufficient and proper lubrication. For the electrical system, the integrity of electrical components, secure wiring connections, and insulation resistance must be verified to ensure compliance with requirements. All components must meet design specifications without defects or damages.
Preparation of Electric Hoist and Related Accessories
As an essential supporting device for the crane, the preparation of the electric hoist is equally critical. Components such as the hoist body, wire rope, hook, and controller must be inventoried and inspected. The structural integrity of the hoist body should be checked for deformations or damages, and the tightness of components, especially bolts and nuts, must be ensured. The wear condition of the wire rope, such as broken wires or deformations, and the hook’s wear condition must meet safety standards. For critical electrical components like the controller, their performance stability and wiring integrity must be verified. Additionally, necessary connectors, fasteners, and safety protection devices should be prepared according to installation requirements. These include various specifications of bolts, nuts, washers, and safety devices like overload protectors and limit switches.
Preparation of Installation Tools and Equipment
To ensure a smooth installation process, the required installation tools and equipment must be prepared in advance. This includes, but is not limited to, lifting machinery, welding equipment, power tools, and measuring instruments. When preparing lifting machinery, ensure its stable and reliable performance, and that operators are qualified and experienced. Welding equipment should be checked for stable power connections and the integrity of accessories like welding guns and clamps. Power tools such as drills and grinders should also be inspected and maintained. Measuring instruments like levels and steel tapes must be checked for accuracy and reliability. All tools and equipment should be calibrated and tested to ensure stable and safe performance.

On-Site Preparation and Layout
Site Cleaning and Planning
Before installation, the installation site must be thoroughly cleaned to remove all debris and obstacles unrelated to the installation, including ground residues, hanging objects, cables, and other materials that may hinder the installation process or pose safety hazards. The site space should be rationally planned based on the equipment’s dimensions, weight, and installation requirements, determining key areas such as equipment foundation positions, lifting channels, and operator spaces. Clear transportation channels should be established to ensure smooth entry and exit of equipment and lifting tools. A stable working platform should be set up to meet the standing and operational needs of installers. Prominent safety warning signs, such as “No Smoking” and “Danger Zone,” should be placed at key locations to remind on-site personnel of safety precautions and potential risks.
Determination of Crane Installation Position
During installation, the optimal installation position of the crane must be determined based on the actual structural load-bearing capacity of the plant, the equipment’s dimensions, and specific operational requirements. This step involves considering factors such as equipment lifting paths, connection methods, and power supply to ensure the crane provides sufficient lifting height and coverage during operation. The installation must strictly follow design drawings and standards, ensuring precise installation of the main girder, end girders, and running rails. Accurate measurement and marking techniques should be used to ensure all parameters meet design requirements, guaranteeing the crane’s stability and safety during subsequent use.
Safety Protection Measures
To ensure the safety of on-site personnel and equipment, comprehensive safety protection measures must be implemented at the installation site. This includes, but is not limited to, setting up safety nets around the site to prevent injuries from falling objects, installing guardrails around hazardous areas to prevent unauthorized access, and placing warning lights and alarms to alert personnel of potential hazards. Additionally, detailed safety operation procedures and emergency plans should be developed based on the site’s actual conditions, specifying safety precautions and response measures during installation to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment throughout the process.
Installation Steps for Single Girder Overhead Crane
Assembly of Main Girder and End Girders
According to design drawings and technical requirements, the main girder and end girders should be precisely assembled. First, inspect the main girder and end girders to confirm their dimensions, shapes, and materials meet design specifications. Then, pre-assemble the main girder and end girders as per the drawings, using high-strength bolts or welding to ensure a secure connection. During the connection process, maintain horizontal and vertical alignment to ensure the crane’s stability and safety.
Installation of Hoisting Mechanism
Install the hoisting mechanism on the main girder, ensuring proper installation and alignment of components such as the drum, wire rope, and hook. During installation, check the drum’s rotation flexibility, the wire rope’s secure fastening, and the hook’s smooth lifting. Additionally, commission the hoisting mechanism’s electrical control system to ensure stable and accurate operation. During commissioning, verify the control system’s sensitivity and reliability to ensure the crane’s safety and stability.
Installation of Traveling Mechanism
Install the traveling mechanism, including the drive unit, wheel sets, and rails. During installation, ensure the wheel sets’ horizontal and vertical alignment to guarantee smooth crane movement on the rails. Check the drive unit’s installation position and the transmission mechanism’s flexibility and reliability. After installation, commission and test the traveling mechanism to ensure smooth and accurate operation.
Installation and Commissioning of Electrical System
Install the crane’s electrical system according to electrical design drawings and standards. This includes the installation and wiring of components such as the control cabinet, cables, motors, and sensors. During installation, ensure correct and reliable wiring to prevent electrical faults. Subsequently, commission and test the electrical system, including the control system, protection devices, and display units. During commissioning, verify the system’s control accuracy, operational reliability, and display clarity.
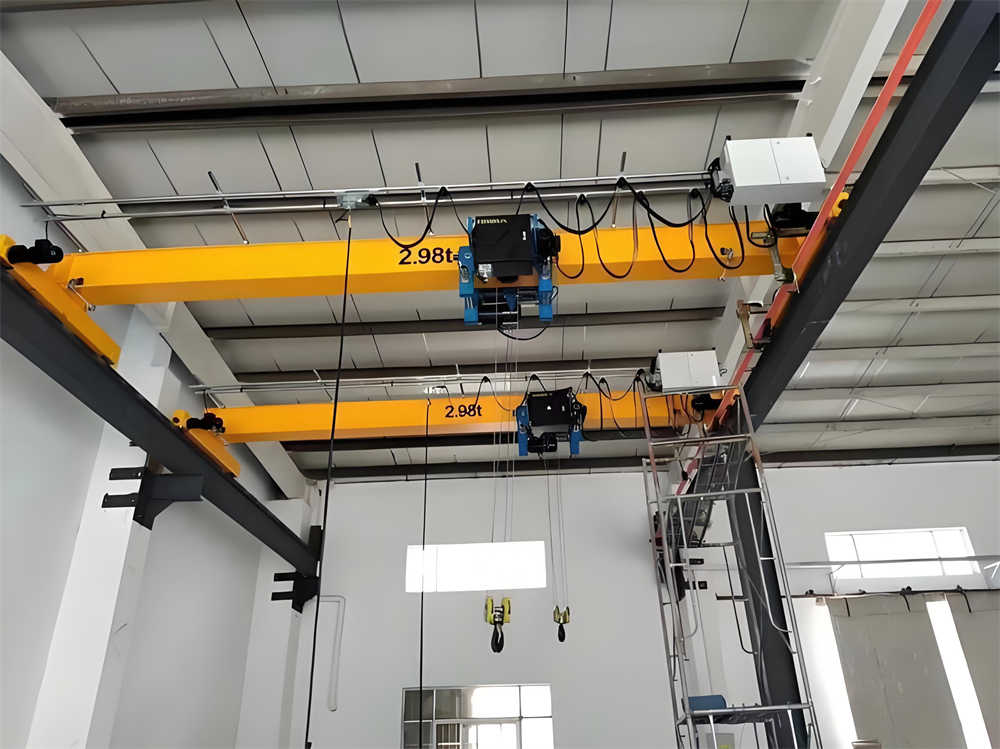
Installation and Commissioning of Electric Hoist
Assembly and Inspection of Electric Hoist
Before formal installation, assemble and inspect the electric hoist. Ensure all components, such as the hoisting mechanism, motor, reducer, drum, pulley block, traveling wheel set, and electrical control system, are correctly installed and securely fastened. Check electrical connections to ensure all terminals and cables are securely connected without loose or short circuits. Conduct a no-load test run to verify the hoist’s smooth operation, braking performance, and the effectiveness of safety protection devices. Observe the hoist’s performance during startup, operation, and stopping, confirming the braking system’s effectiveness under various conditions and the proper functioning of overload and limit protection devices.
Lifting and Positioning of Electric Hoist
Use appropriate lifting machinery to hoist the electric hoist to the designated position. During lifting, maintain the hoist’s balance to prevent damage from swinging or tilting. Precisely adjust the hoist to ensure a secure and accurate connection with the crane’s main girder. During installation, use specialized tools for precise adjustments to ensure the hoist’s alignment with the main girder and the secure fastening of all connectors, such as bolts and nuts.
Commissioning of Electric Hoist
Conduct a load test run of the electric hoist to check its performance under different working conditions. This includes testing and adjusting parameters such as lifting speed, traveling speed, and braking distance. During the load test run, precisely measure and adjust the hoist’s performance parameters. The lifting speed test confirms the hoist’s lifting speed meets design requirements; the traveling speed test checks the hoist’s speed stability on the rails; the braking distance test verifies the hoist’s braking effectiveness and safety. Additionally, verify the functionality of safety protection devices to ensure their sensitivity and reliability. During the load test run, also verify the functionality of various safety protection devices, such as overload and limit protection. Simulate extreme conditions to ensure these devices respond correctly and promptly, ensuring the system’s safety and stability.

Safety Inspection and Acceptance
Installation Quality Inspection
After completing the crane installation, conduct a comprehensive and detailed installation quality inspection. This includes inspecting the welding quality and bolt tightness of the main girder and end girders to ensure they meet design strength requirements. Use professional measurement tools to verify the horizontal and vertical alignment of the main girder and end girders, ensuring structural stability and dimensional accuracy. Dynamically test the hoisting and traveling mechanisms to observe their smoothness, stability, and load response. Check the wear condition of mechanical transmission components, such as gears and chains, ensuring they are within acceptable limits without abnormal noise or vibration. Inspect the electrical system’s wiring terminals, switch cabinets, and controllers for secure connections and accurate logic control. Conduct simulated operational tests to verify the electrical system’s functionality and safety.
Safety Performance Testing
Regular safety performance testing of the crane is crucial during its application. This includes evaluating the crane’s load-bearing capacity through professional mechanical tests to ensure it meets design requirements, preventing structural damage from overloading or fatigue. Stability testing is also essential, simulating actual working conditions to assess the crane’s risk of tipping under various loads, ensuring sufficient stability. Braking performance testing is equally important, measuring braking distance and deceleration under no-load and load conditions to ensure quick and effective stopping in emergencies. Additionally, verify the effectiveness of safety protection devices, such as limit switches, emergency stop buttons, guardrails, and sweep guards, ensuring they provide adequate protection when needed.
Acceptance Standards and Procedures
To ensure the crane’s installation quality and safety performance meet design intentions and industry standards, rigorous acceptance standards and procedures must be established. Form an acceptance team including the installation unit, user unit, supervision unit, and industry experts. During acceptance, use on-site inspections, performance tests, and document reviews to comprehensively verify the crane’s installation quality. On-site inspections include checking the overall appearance and component installation positions; performance tests cover functional parameters such as lifting capacity, speed, and precision; document reviews include installation records, product certificates, and test reports.
Installation Construction Precautions
Personnel Safety and Protection Measures
During installation, strict adherence to detailed safety operation procedures and protection measures is essential to ensure the safety and health of workers. Each worker should be equipped with and correctly use personal protective equipment, such as safety helmets, harnesses, goggles, and masks, to prevent injuries from slips, falling objects, or flying debris. Establish a comprehensive on-site safety management system, appoint dedicated safety supervisors, and conduct regular safety training to enhance workers’ safety awareness and operational skills. Set up prominent safety warning signs and barriers to prevent unauthorized access and ensure workers are aware of the site’s conditions.
Equipment Protection and Maintenance
During installation and commissioning, proper protection and regular maintenance of the equipment are crucial. Use protective packaging materials and foam pads to minimize mechanical damage during transportation and lifting. Inspect precision components or vulnerable parts before and after installation to ensure no scratches or impacts, preventing performance degradation or failure. Implement a regular maintenance plan, including cleaning, lubrication, and wear inspections, to keep the equipment in optimal condition and extend its service life.
Emergency Plans and Response Measures
Develop detailed emergency plans and response measures for potential incidents during installation, such as equipment failures, operational errors, power outages, adverse weather, or fire accidents. Emergency plans should include command systems, rescue teams, communication procedures, and evacuation routes to ensure a swift and effective response in emergencies. Train workers in emergency response through theoretical instruction and practical drills, enhancing their ability to react quickly and resolve issues independently, ensuring personnel safety and project success.
Conclusion
The installation and construction plan for single girder overhead cranes and electric hoists is a complex and systematic project involving multiple steps and procedures. Through meticulous planning and strict operations, high-quality installation can be achieved, ensuring the equipment’s stability and safety during subsequent use. In a highly industrialized country like Singapore, the installation and maintenance of lifting equipment are particularly important. This article aims to provide a comprehensive and practical installation guide for relevant personnel, supporting the continuous development of Singapore’s industry.